Electric vehicle (EV) charging stations are devices that provide power supply to electric vehicles, similar to fuel pumps at traditional gas stations.
They convert electrical energy from the external power grid into a form suitable for the EV battery and transmit it to the vehicle through specific interfaces.
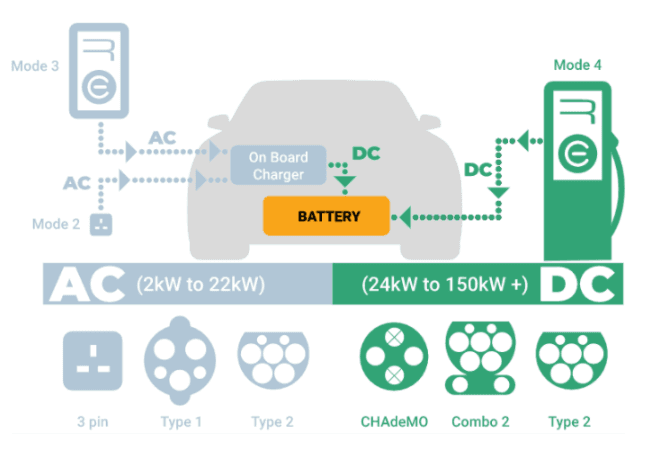
Depending on the charging method, charging stations can be categorized into AC charging stations (slow charging) and DC charging stations (fast charging). Below is a detailed introduction to the definition, types, working principles, and functions of EV charging stations.
1. Definition of EV Charging Stations
An EV charging station is a power conversion device that connects the power grid and the EV battery, with the primary function of charging electric vehicles.
The charging station connects to the car via an EV charging interface and delivers either AC or DC electricity to the onboard battery. Charging stations are commonly installed in public areas, commercial parking lots, home garages, and highway service areas, providing convenience for EV users to charge their vehicles at any time.
2. Types of EV Charging Stations
Charging stations are mainly divided into AC charging stations and DC charging stations based on the charging method:
2.1. AC Charging Stations (AC Charging, Slow Charging)
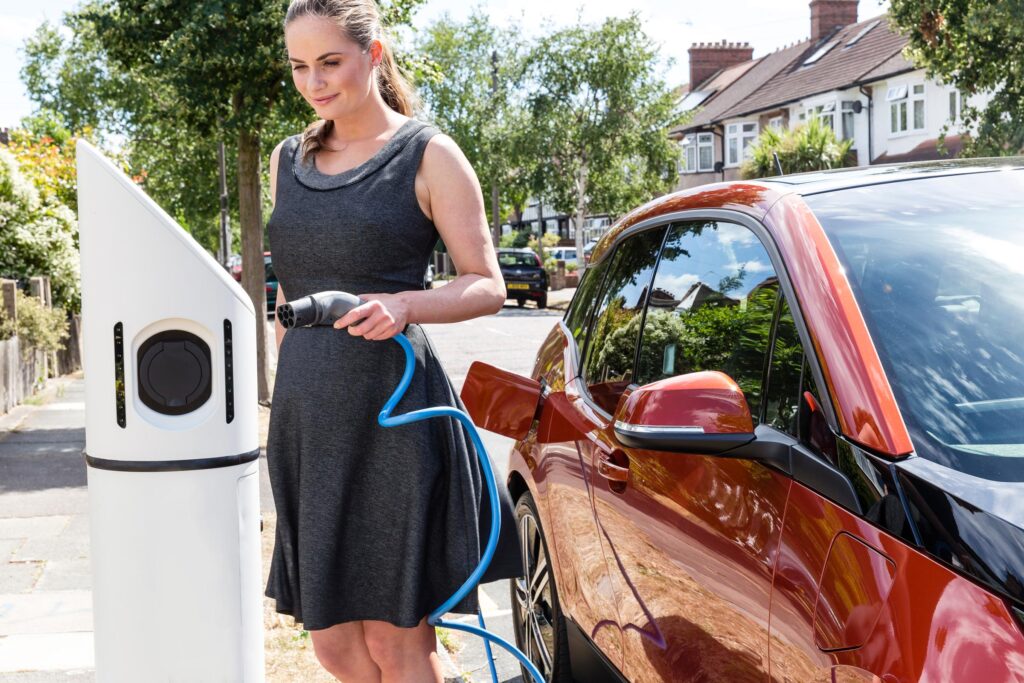
AC charging stations, including portable and fixed charging stations, are typically referred to as slow chargers. They deliver power to the vehicle via standard power sources (single-phase or three-phase AC). This type of charging station relies on the vehicle’s onboard charger (OBC, On-Board Charger) to convert AC power to DC power for battery charging.
- Output Current: AC charging stations output AC power, with typical power ranging from 3.7 kW to 22 kW, depending on grid voltage and the station’s specifications.
- Working Principle: The AC charging station transmits AC power from the grid to the EV via a charging cable. The onboard charger (OBC) converts the AC power to DC, which charges the battery. Since the onboard charger has limited power capacity, charging speeds are relatively slow, making it suitable for long-term parking or overnight charging.
2.2. DC Charging Stations (DC Fast Charging, Fast Charging)
DC charging stations, commonly referred to as fast chargers, can deliver direct current (DC) power directly to the vehicle’s battery without relying on the onboard charger, allowing for higher power output and faster charging speeds. DC charging stations are typically used at highway service areas, shopping malls, and other locations where quick charging is needed.
- Output Current: DC charging stations output DC power, with charging power ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW, and future ultra-high-power fast charging stations may even reach 500 kW or more.
- Working Principle: DC charging stations integrate high-power conversion equipment that transforms AC power from the grid into DC power and then transmits it directly to the EV battery through a dedicated DC charging interface. Since it bypasses the onboard charger, DC charging stations can significantly shorten the charging time.

3. Working Principle of EV Charging Stations
The working process of an EV charging station can be broken down into the following steps:
3.1. Grid Connection
The charging station connects to the power grid through transformers and distribution systems. The power is transmitted from the grid to the charging station’s internal power conversion system via cables.
3.2. Charging Mode Selection
The station selects AC or DC mode based on its type. AC charging stations deliver AC power directly to the vehicle, which is handled by the onboard charger, while DC charging stations convert AC power to DC internally.
3.3. Communication Protocol and Interface Connection
Before charging starts, the station and the EV must communicate using a protocol handshake. The charging station detects the vehicle’s battery status, charging needs, and supported power levels to ensure current matching. During this process, the EV and charging station exchange real-time information via CAN (Controller Area Network) or other protocols.
3.4. Power Transmission and Charging Monitoring
The charging station begins transmitting power to the EV battery, continuously monitoring current, voltage, temperature, and other parameters to ensure safe and stable charging. The vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS) also communicates with the charging station to adjust current levels and prevent issues like battery overheating or overcharging.
3.5. Charging Completion and Disconnection
Once the EV battery reaches the desired charge level or full capacity, the charging station automatically stops charging. The user can confirm the charging completion through a charging card or mobile app, after which they can disconnect the charging interface. The charging process is then complete.

4. Functions of EV Charging Stations
EV charging stations not only provide power to vehicles but also offer the following functions:
- Power Metering: Charging stations have power metering functions that accurately record electricity consumption during the charging process, allowing users to pay for the electricity used.
- Smart Control: Many modern charging stations offer smart control features, enabling users to schedule, start, monitor, and stop charging via mobile apps or charging platforms, allowing remote management of the charging process.
- Load Balancing: Some advanced charging stations have load balancing functions, dynamically adjusting power output to ensure that multiple vehicles can charge simultaneously without overloading the grid.
- Safety Protection: Charging stations include safety features such as overcurrent protection, short circuit protection, and leakage protection, ensuring safe operation during the charging process.
- Compatibility: Most public charging stations support multiple standard interfaces such as CCS, CHAdeMO, and GB/T, ensuring that different brands and types of EVs can use the corresponding charging stations.
- Energy Storage Management: In the future, as the number of EVs increases, vehicle batteries may be used as energy storage systems in coordination with charging stations to store and release energy.

5. Future Trends in EV Charging Stations
- Ultra-High-Power Charging: Future charging stations will support higher charging power, potentially reaching 500 kW or more, reducing charging time to just a few minutes.
- Smart Charging Networks: Charging stations will interact with the power grid, smart meters, and energy management systems, efficiently distributing power resources and enabling Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) functionality, allowing EVs to return power to the grid.

EV charging stations are vital infrastructure for electric vehicles, not only providing power to vehicles but also offering smart monitoring, safety protection, and payment functions. As the EV market rapidly grows, charging station technology continues to advance. In the future, ultra-high-power charging, wireless charging, and smart charging networks will become important development directions. Understanding how EV charging stations work and their functions is essential for both EV owners and industry professionals.



