The charging interfaces and standards for electric vehicles (EVs) vary by region and market. As the EV market rapidly evolves, countries and regions have gradually established corresponding charging standards to ensure that EVs can charge smoothly at various facilities. Below is a detailed introduction to the main EV charging interfaces and standards worldwide:
1. Types of Charging Interfaces
1.1. AC (Alternating Current) Charging Interface
AC charging is generally used for slow charging and is common in home or public charging stations. The main interface standards include:
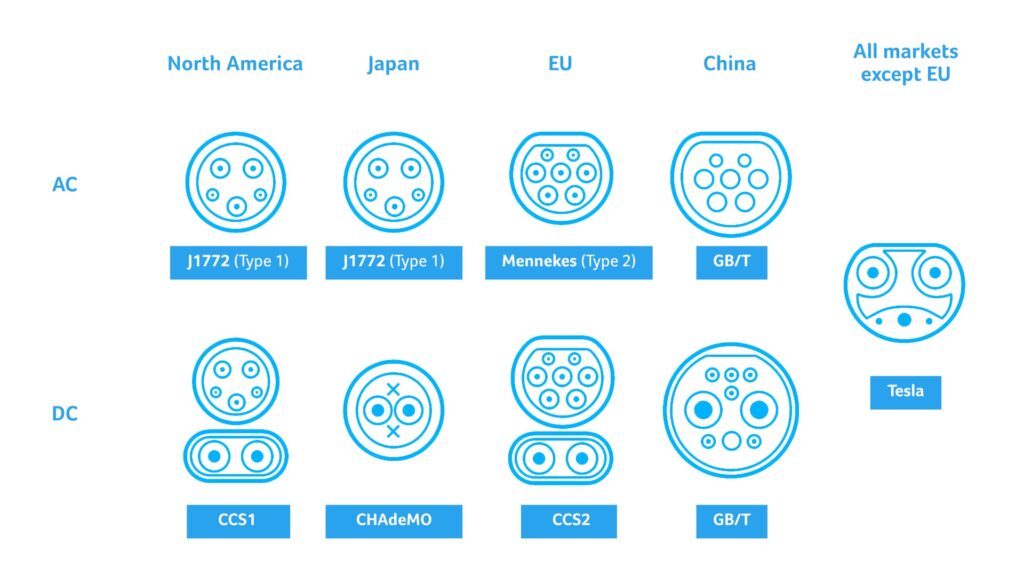
- Type 1 (SAE J1772): This interface is mainly used in North America, Japan, and other markets, commonly found in AC slow chargers. It uses a single-phase interface, with a typical maximum charging power of 7.2kW. IEVTIME’s AC chargers can reach a maximum charging power of 9.6kW.
- Type 2 (IEC 62196-2, Mennekes): The Type 2 interface is mainly used in Europe. It supports both single-phase and three-phase power, with charging power up to 22kW, suitable for home and public AC charging stations.
- GB/T (China National Standard): The GB/T interface is the national standard in China, used primarily in the Chinese market. It supports both single-phase and three-phase power, with charging power up to 22kW, suitable for home and public AC charging stations.
- Tesla (J 3400, NACS): Tesla’s proprietary interface supports both AC and DC charging and is mainly used in the North American market. Outside North America (in Europe and China), Tesla follows local standards, using CCS2 or GB/T standards.
1.2. DC (Direct Current) Fast Charging Interface
DC charging is used for fast charging, significantly reducing charging time, making it suitable for highway charging stations or situations requiring quick charging. The main interface standards include:
- CHAdeMO: CHAdeMO is a fast-charging standard initiated by Japan, mainly used in the Japanese market, with some usage in North America and Europe. It is designed for high-voltage DC charging, with typical power between 50kW and 100kW. New versions support up to 400kW.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): The CCS interface is an extension of the Type 2 interface, integrating both AC and DC charging functions. CCS is the dominant fast-charging standard in Europe and North America. CCS1 is primarily used in North America, while CCS2 is mainly used in Europe. The DC charging power can reach up to 350kW, supporting high-power fast charging.
- GB/T (China National Standard): The GB/T interface is the national standard in China, mainly used in the Chinese market. The GB/T standard includes both AC and DC interfaces, with the DC interface supporting up to 250kW, and future upgrades may extend this to 500kW or more.

2. Overview of Global Charging Standards
2.1. North America
The main charging standards in North America include Type 1 (J1772) for slow charging and CCS1 for fast charging. North America also features Tesla’s proprietary interface, but Tesla is gradually opening its Supercharger network to support CCS1. The usage of CHAdeMO is declining in North America, with CCS1 becoming the dominant standard.
2.2. Europe
Europe’s main standards are Type 2 (AC) and CCS2 (DC). The European Union mandates that all new electric vehicles and charging stations must be compatible with Type 2 and CCS2, making this standard widespread across Europe. Additionally, the demand for fast charging is high in Europe, with many stations supporting charging power up to 350kW.
2.3. Japan
Japan’s EV charging market mainly relies on the CHAdeMO standard, especially for fast charging. Although most vehicles and infrastructure in Japan use CHAdeMO, as CCS2 becomes more widespread globally, more dual-standard compatible charging stations may be introduced in the future.
2.4. China
China’s charging interfaces and standards are dominated by GB/T, which includes both AC slow charging and DC fast charging interfaces. GB/T DC fast charging power continues to increase, with future support for faster charging speeds. Additionally, with the globalization of the Chinese market, many automakers and charging station providers are offering products compatible with both CCS2 and GB/T standards to meet global demands.

3. Charging Interface Choices of Major Automakers
- Tesla: In the North American market, Tesla uses its proprietary interface but has gradually begun supporting CCS1 in its Supercharger network. In Europe and China, Tesla vehicles and charging stations use CCS2 and GB/T interfaces, adhering to local standards.
- Volkswagen, BMW, Mercedes, etc.: These European automakers typically use Type 2 and CCS2 interfaces, supporting high-power fast charging. Porsche, a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group, already supports fast charging up to 270kW.
- Nissan, Mitsubishi: Nissan and Mitsubishi, among other Japanese brands, primarily use the CHAdeMO interface, especially in the Japanese market. However, as CCS becomes more widespread, some models have begun supporting CCS.
In summary, global EV charging interfaces and standards are continuously evolving. Although standards vary by region, there is a clear trend toward global unification. Understanding these charging standards is essential for those working in the EV charger industry.



